Mastering the Test Pyramid for Modern QA
Software quality can’t be left to chance. Testing isn’t just about catching bugs before release, it’s what makes sure your application works the way users expect. Without a well-defined testing approach, teams risk spending more time firefighting issues in production than building new features.
The real challenge is that not all tests deliver the same value. Some are fast and reliable, while others are slower, resource-heavy, and harder to maintain. Relying on the wrong mix of tests can slow down release cycles, waste effort, and still allow critical bugs to slip through.
This is where the test pyramid becomes essential. It is more than just a diagram, it is a framework that helps software teams structure their testing strategy. By putting the right emphasis on the right type of tests, teams can save time, reduce costs, and release software with greater confidence. In this blog, we will dive deep into what the test pyramid is, why it matters, and how you can apply it to your development workflow with the help of Quash.
Why Testing Deserves Center Stage
Let’s face it, testing often feels like the longest part of the development cycle. But skipping it is like skipping safety checks before a flight. Sure, the plane might take off, but the risks are huge. Without proper testing, your users become the testers, which is the last thing you want.
Proper testing ensures that bugs are caught before they reach production. This not only prevents embarrassing glitches but also saves teams from late-night fixes, costly rollbacks, and negative user reviews. By investing in the right testing strategy, you protect both your product and your reputation.
When done right, testing also shortens feedback loops, reduces debugging time, and boosts developer confidence. Teams know their code works as intended, which means they can release faster without second-guessing every change. This is exactly why the test pyramid exists. It is a smarter way to test that reduces bottlenecks while improving quality.

Get the Mobile Testing Playbook Used by 800+ QA Teams
Discover 50+ battle-tested strategies to catch critical bugs before production and ship 5-star apps faster.
From Manual Testing to Test Automation
If we look back at the history of software development, testing was once almost entirely manual. QA engineers had to click through every feature, validate every workflow, and document results by hand. It was time-consuming, repetitive, and inevitably prone to human error.
The shift to test automation completely changed the game. Automated tests run in minutes, repeat consistently across environments, and scale easily as the application grows. Teams no longer had to rely solely on manual testers to validate every small change.
However, automation by itself is not the full solution. If your test strategy is not structured, you may still end up with slow pipelines, flaky tests, or coverage gaps. This is where the test pyramid becomes critical. It shows teams how to prioritize different types of tests so automation actually speeds things up instead of slowing them down.
The Test Pyramid Explained
The test pyramid, first introduced by Mike Cohn, is a simple but powerful model for structuring tests. Imagine a real pyramid. The base is wide, representing tests that are cheap, reliable, and should be run most frequently. The middle is narrower, representing tests that are slightly slower and more complex. Finally, the top is small, representing expensive, high-level tests that should be limited in number.
The pyramid visually communicates one important rule: the majority of your tests should be at the lower levels. If too many of your tests live at the top, your testing strategy becomes slow, expensive, and fragile. If most of your tests are at the base, you gain speed, coverage, and confidence.
Breaking Down the Three Layers
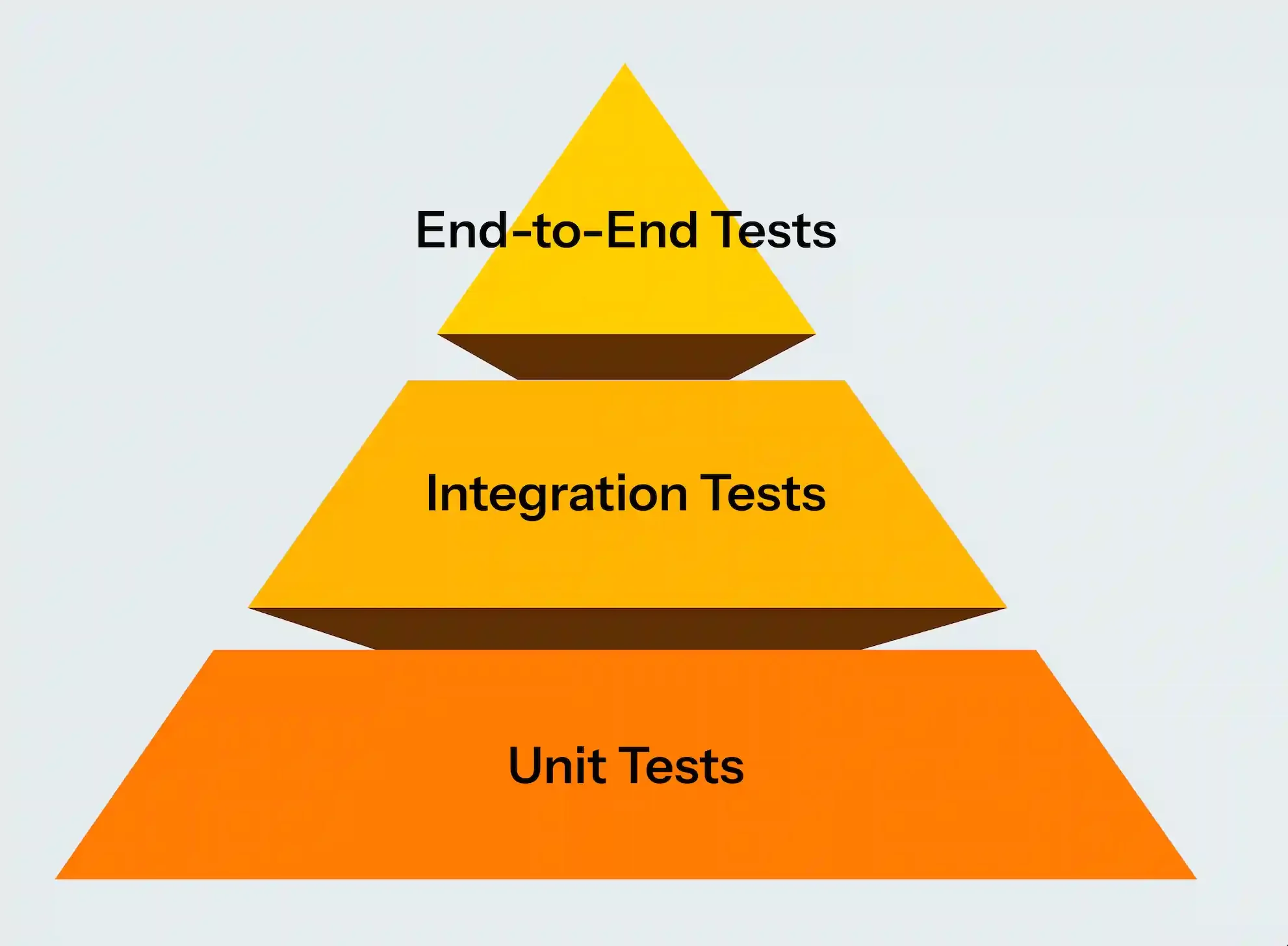
1. Unit Tests (Foundation)
Unit tests form the foundation of the pyramid. These are small, isolated tests that focus on individual pieces of code such as functions, methods, or components. Since they only test one thing at a time, they are extremely fast and cost-effective.
The main advantage of unit tests is that they catch bugs early in the development cycle. By running unit tests on every build, developers can be sure that each new piece of code works as intended. When the foundation is strong, the rest of the testing layers become easier to manage.
In short, unit tests are the safety net for developers. They reduce debugging time, prevent regressions, and provide confidence that changes won’t break existing functionality.
2. Integration Tests (Middle Layer)
While unit tests focus on small components, integration tests check how different parts of the system work together. These tests are crucial because even if individual pieces of code work perfectly, they may fail when combined.
For example, your login system might work in isolation and your database might work in isolation, but what happens when you connect the two? Integration tests catch issues such as mismatched data formats, broken APIs, or misconfigured services.
These tests are more complex than unit tests and require additional resources, but they ensure that the different modules of your application communicate correctly. Without integration tests, you risk shipping software that looks fine on the surface but breaks when real users interact with it.
3. End-to-End (E2E) Tests (Top Layer)
At the top of the pyramid are end-to-end tests (E2E tests). These simulate actual user journeys and validate whether your application works from start to finish. For example, an E2E test might cover the entire process of logging in, adding an item to the cart, and checking out.
E2E tests are incredibly valuable because they show you the application from the user’s perspective. But they are also slow, resource-intensive, and difficult to maintain. That is why the test pyramid recommends keeping them limited.
Instead of testing everything with E2E, focus on high-value workflows. Make sure that your most critical user paths are covered, but rely on unit and integration tests for the bulk of your testing.
Why the Test Pyramid Works
The power of the test pyramid lies in how it balances speed, cost, and coverage. Here are the main benefits teams gain:
Early bug detection: Unit tests catch errors before they spread to higher layers.
Efficiency: Fast lower-level tests provide instant feedback to developers.
Cost-effectiveness: Reducing dependence on heavy E2E tests saves time and resources.
Faster releases: Quicker feedback loops keep CI/CD pipelines flowing smoothly.
Stronger coverage: A mix of tests across levels ensures the entire system is validated.
In other words, the test pyramid is not just about testing more, it is about testing smarter.
Putting the Pyramid Into Practice
To implement the pyramid effectively, start at the base and work your way up.
Unit tests should make up the majority of your suite. Keep them automated, isolated, and integrated into every build.
Integration tests should focus on the most critical connections between components. Mock external dependencies when possible to avoid unnecessary flakiness.
E2E tests should validate only the most important workflows on real devices. Schedule them strategically so they do not slow down the entire pipeline.
When balanced correctly, this approach gives you strong coverage without overwhelming your team or infrastructure.
Challenges With the Test Pyramid
Even though the test pyramid is a clear framework, applying it in real-world projects can be tricky. Common challenges include:
Test maintenance as the codebase grows.
Flaky tests that fail inconsistently at the integration or E2E level.
Environment setup difficulties for realistic test conditions.
Execution time bottlenecks when test suites become too large.
Finding the right balance between unit, integration, and E2E tests.
These challenges are why many teams struggle to apply the pyramid consistently. But this is also where Quash steps in to make life easier.
How Quash Makes It Easier
The Quash platform is designed to simplify and accelerate testing across all levels of the pyramid. Instead of manually managing test suites and struggling with flaky scripts, Quash brings AI-powered automation to the table.
AI-generated unit tests help teams catch bugs early without writing endless scripts.
Smart integration testing runs seamlessly across real devices and networks.
Efficient E2E testing ensures critical user journeys are covered without overloading the pipeline.
Flakiness detection and self-healing tests keep your suite reliable and trustworthy.
CI/CD integration ensures tests run automatically in your workflow without extra effort.
By combining the test pyramid strategy with Quash, teams can finally achieve the balance of speed, quality, and cost-effectiveness that modern software development demands.
Final Thoughts
The test pyramid is more than a theory. It is a practical framework that ensures your testing efforts are focused in the right place. By emphasizing fast unit tests, targeted integration tests, and lean E2E tests, teams can prevent bugs, reduce costs, and ship high-quality software faster.
With Quash, implementing the test pyramid becomes far easier. From AI-generated tests to self-healing automation, Quash helps teams avoid common pitfalls and maintain confidence in every release.
Testing does not need to be a bottleneck. With the right strategy and the right tools, it becomes your biggest advantage.
FAQs
Q1. Is the test pyramid still relevant in 2025? Yes. The test pyramid continues to be one of the most effective frameworks for structuring software tests. While tools and practices evolve, the principle of focusing on unit and integration tests before E2E remains highly relevant.
Q2. How many end-to-end tests should a team write? There is no fixed number, but the best practice is to cover only the most critical user journeys with E2E tests. Too many will slow your CI/CD pipeline, so balance them with faster unit and integration tests.
Q3. Can the test pyramid work in agile environments? Absolutely. Agile teams benefit from fast feedback loops, and the pyramid supports this by emphasizing quick, automated unit tests while keeping slower tests limited.
Q4. How does Quash fit into the test pyramid model? Quash makes it easier to implement the pyramid by automating unit, integration, and E2E tests. With features like AI-generated scripts, real-device testing, and flakiness detection, Quash reduces the challenges of managing tests across layers.
Q5. What happens if a team ignores the test pyramid? Without the pyramid, teams often rely too heavily on manual or E2E tests. This creates slow pipelines, higher costs, and unreliable test results. Over time, this slows down releases and increases the risk of bugs slipping into production.




