Design Meets QA
As mobile applications become increasingly complex and user expectations continue to soar, the traditional boundaries between design and quality assurance are dissolving. The most successful mobile apps today aren't just functionally sound—they're intuitive, accessible, and genuinely delightful to use. This convergence of design thinking and QA methodologies represents a fundamental shift in how we approach mobile app development, one that prioritizes user experience at every stage of the testing process.
The Evolution of Mobile App Testing in 2025
Mobile app testing has evolved dramatically from its early days of simple functionality checks. Today's testing landscape encompasses AI-driven automation, real-device testing across thousands of device combinations, and sophisticated user experience validation. The rise of 5G networks, foldable devices, AR/VR applications, and IoT integration has created new testing challenges that traditional QA approaches struggle to address effectively.
The integration of user-centered design (UCD) principles into QA processes represents a paradigm shift from reactive bug-finding to proactive user experience optimization. This approach recognizes that quality isn't just about the absence of defects—it's about creating mobile experiences that truly serve user needs and exceed their expectations.

Get the Mobile Testing Playbook Used by 800+ QA Teams
Discover 50+ battle-tested strategies to catch critical bugs before production and ship 5-star apps faster.
Understanding User-Centered Design in Mobile Testing Context
User-centered design is an iterative design process that focuses on users and their needs throughout the development lifecycle. When applied to mobile app testing, UCD transforms quality assurance from a technical validation exercise into a human-centered practice that ensures apps not only work correctly but work beautifully for real users.
The core principles of UCD in mobile testing include:
Empathy-Driven Testing Strategies
Traditional testing often focuses on technical specifications and edge cases. Design thinking introduces empathy as a foundational element, requiring QA teams to deeply understand user perspectives, pain points, and contexts of use. This means testing not just what users might do, but understanding why they do it and how they feel throughout the process.
Modern QA teams are incorporating ethnographic research methods, user interviews, and observational studies directly into their testing workflows. This approach helps identify usability issues that automated testing might miss, such as confusing navigation patterns or accessibility barriers that affect specific user groups.
Iterative Validation Throughout Development
Rather than waiting until development completion to begin comprehensive testing, design-driven QA integrates validation activities throughout the entire development process. This "shift-left" approach, combined with design thinking principles, ensures that user feedback informs not just bug fixes but fundamental design decisions.
The integration involves creating rapid prototypes for early user testing, conducting continuous usability validation during development sprints, and maintaining feedback loops between design, development, and QA teams. This collaborative approach has been shown to reduce development costs by up to 100 times when issues are caught early rather than in production.
Mobile-Specific Design Challenges and QA Integration
Mobile applications present unique challenges that require specialized design thinking approaches within QA processes. The diversity of devices, operating systems, network conditions, and usage contexts creates a complex testing matrix that traditional methods struggle to address comprehensively.
Device Fragmentation and User Context
With thousands of device combinations in the market, design-centered QA approaches prioritize testing on devices and configurations that matter most to actual users. This involves using analytics and user research to identify the most critical device combinations, rather than attempting to test everything equally.
AI-powered testing tools are increasingly being used to intelligently select device combinations and network conditions that represent real user scenarios. These tools can simulate user behavior patterns and adapt testing protocols based on actual usage data, ensuring that QA efforts focus on the most impactful user journeys.
Performance and Accessibility Integration
Performance testing in mobile applications goes beyond traditional load testing to include battery usage, memory consumption, and responsiveness under varying network conditions. Design thinking principles help QA teams understand that performance issues aren't just technical problems—they're user experience failures that can significantly impact app adoption and retention.
Accessibility testing has become a cornerstone of design-driven QA, ensuring applications comply with WCAG guidelines while providing genuinely inclusive experiences. This involves testing with assistive technologies, validating keyboard navigation patterns, and ensuring content is accessible to users with various disabilities.
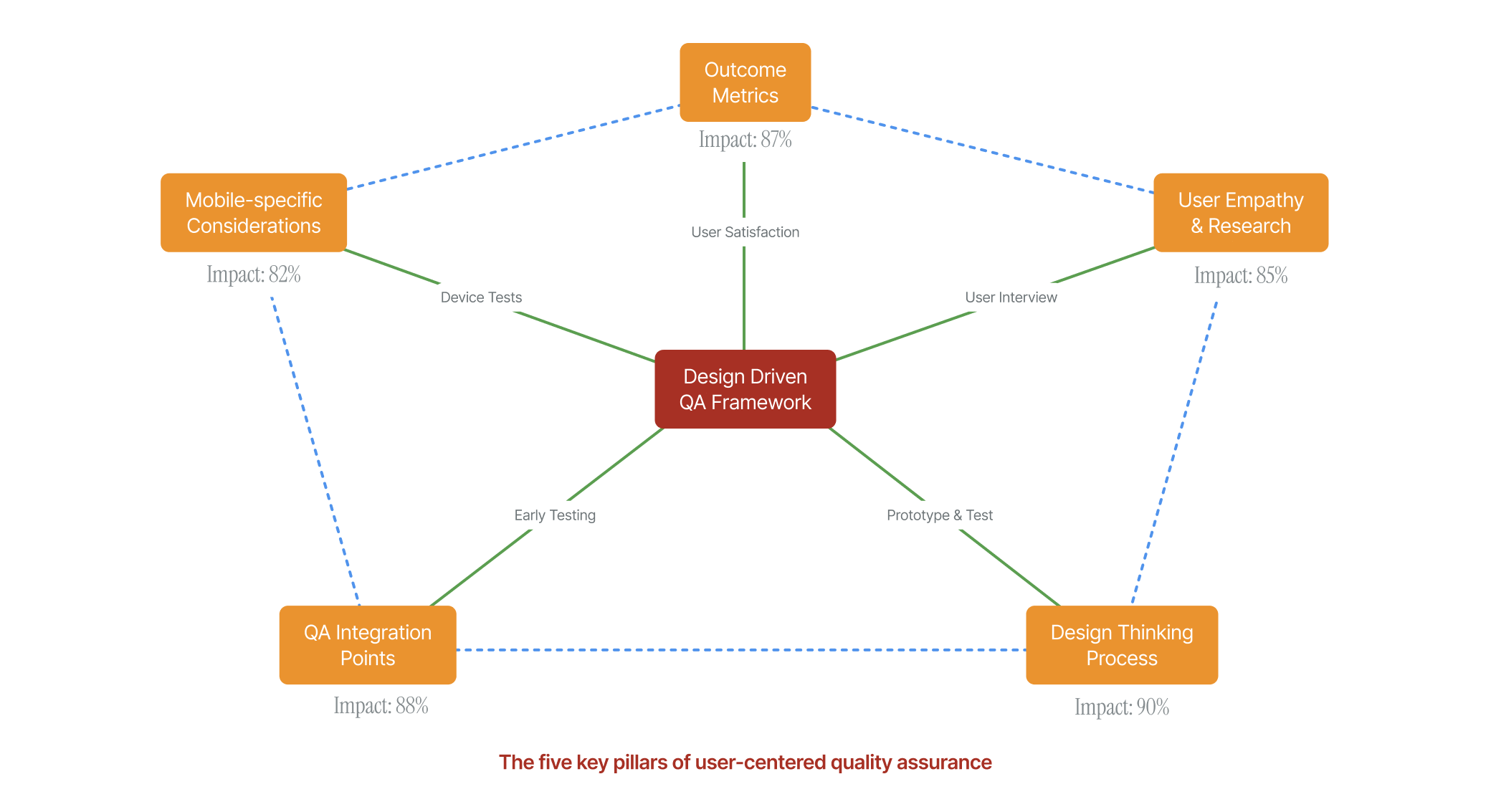
Implementing Design Thinking in Mobile QA Workflows
The practical implementation of design thinking in mobile QA requires structural changes to traditional testing workflows. Successful organizations are adopting frameworks that integrate user research, design validation, and technical testing into cohesive processes.
Early User Research Integration
Leading mobile teams begin their QA processes with comprehensive user research, including persona development, user journey mapping, and contextual inquiry. This research informs not just what to test, but how to prioritize testing efforts and validate that technical implementations align with user expectations.
User interviews and observational studies help QA teams understand real-world usage patterns that might not be captured in traditional test cases. For example, understanding how users actually interact with apps during commutes, in low-light conditions, or while multitasking can reveal usability issues that laboratory testing might miss.
Cross-Functional Collaboration Models
Design-driven QA requires breaking down traditional silos between design, development, and testing teams. Successful implementations involve regular cross-functional workshops where team members collaborate to define testing scenarios based on user needs rather than just technical specifications.
This collaborative approach includes involving designers in test case creation, having QA professionals participate in design reviews, and ensuring that user feedback directly influences both design iterations and testing priorities. The result is more comprehensive testing that validates both technical functionality and user experience quality.
Continuous User Feedback Integration
Modern design-driven QA processes incorporate multiple feedback mechanisms throughout development and post-launch phases. This includes prototype testing with real users, beta testing programs that capture genuine usage patterns, and post-launch monitoring that identifies user experience issues in production environments.
Tools like A/B testing, user session recordings, and in-app feedback collection provide continuous streams of user data that inform both immediate fixes and longer-term product improvements. This approach ensures that quality assurance becomes an ongoing process rather than a pre-launch checkpoint.
AI and Automation in Design-Centered Testing
The integration of artificial intelligence and automation tools is revolutionizing how design thinking principles can be applied at scale in mobile QA processes. These technologies enable more sophisticated user experience testing while reducing manual effort and increasing coverage.
Intelligent Test Generation and Execution
AI-powered testing tools can now generate test cases based on user behavior patterns, automatically adapting to UI changes and predicting potential failure points. These systems learn from user interactions to create more realistic testing scenarios that reflect actual usage patterns rather than idealized test cases.
Self-healing automation capabilities allow test scripts to adapt when application interfaces change, reducing maintenance overhead and ensuring that testing remains focused on user experience validation rather than script maintenance. This is particularly valuable in agile development environments where interface changes are frequent.
Predictive User Experience Analytics
Machine learning algorithms can analyze user behavior data to predict potential usability issues before they impact users. These systems identify patterns in user interactions that might indicate confusion, frustration, or abandonment, allowing QA teams to proactively address experience issues.
Visual testing capabilities powered by AI can detect subtle UI inconsistencies and accessibility issues across different devices and screen sizes. This technology enables comprehensive design validation at scale, ensuring visual consistency and usability across the entire device ecosystem.
Measuring Success in Design-Driven Mobile QA
The success of design-centered QA approaches requires new metrics that go beyond traditional defect counts and test coverage percentages. Organizations implementing these methodologies are developing more comprehensive measurement frameworks that capture user experience quality alongside technical quality.
User Experience Quality Metrics
Successful design-driven QA programs measure user satisfaction through multiple channels, including app store ratings, user retention rates, task completion rates, and time-to-value metrics. These measurements provide direct feedback on whether testing efforts are translating into positive user experiences.
Accessibility compliance scores, performance benchmarks under real-world conditions, and usability heuristic evaluations provide additional dimensions of quality measurement that traditional testing approaches often overlook. These metrics help teams understand not just whether features work, but whether they work well for their intended users.
Business Impact Assessment
The ultimate validation of design-driven QA approaches comes through business impact measurement. Organizations implementing these methodologies report reduced customer support costs, higher user retention rates, faster feature adoption, and improved app store ratings.
Return on investment calculations for design-driven QA must account for both direct cost savings (reduced bug fix costs, faster release cycles) and indirect benefits (improved user retention, higher lifetime value, reduced support burden). These comprehensive measurements help justify the additional investment required for user-centered testing approaches.
Future Trends and Emerging Technologies
The integration of design thinking with mobile QA continues to evolve as new technologies and methodologies emerge. Several trends are shaping the future of this field, with implications for how organizations should prepare their testing strategies.
Augmented and Virtual Reality Testing
As AR and VR applications become mainstream, design-driven QA approaches must adapt to handle immersive experiences that require new types of user validation. Testing these applications requires understanding user comfort, motion sickness prevention, and interaction paradigms that don't exist in traditional mobile interfaces.
QA teams are developing specialized methodologies for testing gesture recognition, spatial interfaces, and cross-device continuity in mixed reality environments. These approaches require close collaboration between UX designers and QA professionals to ensure that immersive experiences are both functional and comfortable for users.
5G and Edge Computing Implications
The rollout of 5G networks creates new opportunities and challenges for mobile app testing, requiring validation of applications that can dynamically adapt to varying network capabilities. Design-driven QA must consider how users experience applications across different network conditions and device capabilities.
Edge computing architectures require testing approaches that validate not just application functionality but also data synchronization, offline capabilities, and seamless transitions between network states. These technical requirements must be validated through the lens of user experience to ensure that architectural complexity doesn't negatively impact usability.
Conclusion: Building a User-Centered Quality Culture
The integration of design thinking principles into mobile app testing represents more than a methodological shift—it's a cultural transformation that places user experience at the center of quality assurance activities. Organizations successfully implementing these approaches report not just improved app quality, but stronger cross-functional collaboration, reduced development costs, and higher user satisfaction.
The key to success lies in recognizing that design-driven QA is not about replacing traditional testing methods but about enriching them with user-centered perspectives and validation approaches. As mobile applications continue to evolve and user expectations rise, the organizations that thrive will be those that can seamlessly blend technical excellence with genuine user empathy.
For QA professionals, designers, and product managers, this represents an opportunity to expand their impact beyond bug prevention to user experience optimization. By embracing design thinking principles, mobile QA teams can become strategic partners in creating applications that don't just work—they delight users and drive business success.
The future of mobile app testing lies not in choosing between technical rigor and user experience focus, but in creating integrated approaches that deliver both. As we move forward, the most successful mobile applications will be those that emerge from development processes where design thinking and quality assurance work hand in hand to create truly exceptional user experiences.